What effect does hip strengthening have on running and single-leg squatting mechanics?
Looking at a study by Richard W. Willy, PT, PhD, OCS, and Irene S. Davis, PT, PhD, FAPTA
Background
Abnormal hip and knee mechanics may be related to a number of running-related injuries, from stress fractures, to IT band syndrome, to patellofemoral pain syndrome (PFPS). PFPS has been linked to abnormal knee movements like excessive hip adduction, hip internal rotation, contralateral pelvic drop (when the opposite side of the pelvis drops), and knee external rotation during running, single-leg squats, single-leg jump landing, and step-downs. Studies suggest that women with PFPS may have weak hip muscles, and though hip strengthening programs have been shown to improve strength, it is not clear whether hip strengthening programs improve abnormal hip and knee mechanics while running and squatting. Though studies have looked at hip strengthening in healthy active females with normal mechanics, only two have looked at that of individuals with abnormal mechanics.
This study by Drs. Willy and Davis aimed to examine the effect of a hip-strengthening program that included movement training for the single-leg squat on hip and knee mechanics during running and squatting in females who exhibited abnormal mechanics during running.
Hypothesis
The researchers hypothesized that peak hip adduction, hip internal rotation, contralateral pelvic drop, and knee external rotation would be reduced during single-leg squats due to the specific neuromuscular reeducation of that activity.
Methods
The researchers included female runners ages 18 – 35, who were running at least 10 km per week, and were required to not do any lower extremity resistance training for at least 90 days before the study. They were assigned to either the control group or the treatment group and were not told which group they had been assigned to. The researchers measured peak hip adduction (HADD) during running and squatting because excessive hip adduction is related to lower extremity injuries in runners. The researchers measured baseline hip abduction and external rotation strength at baseline and after a strengthening program or after the control group.
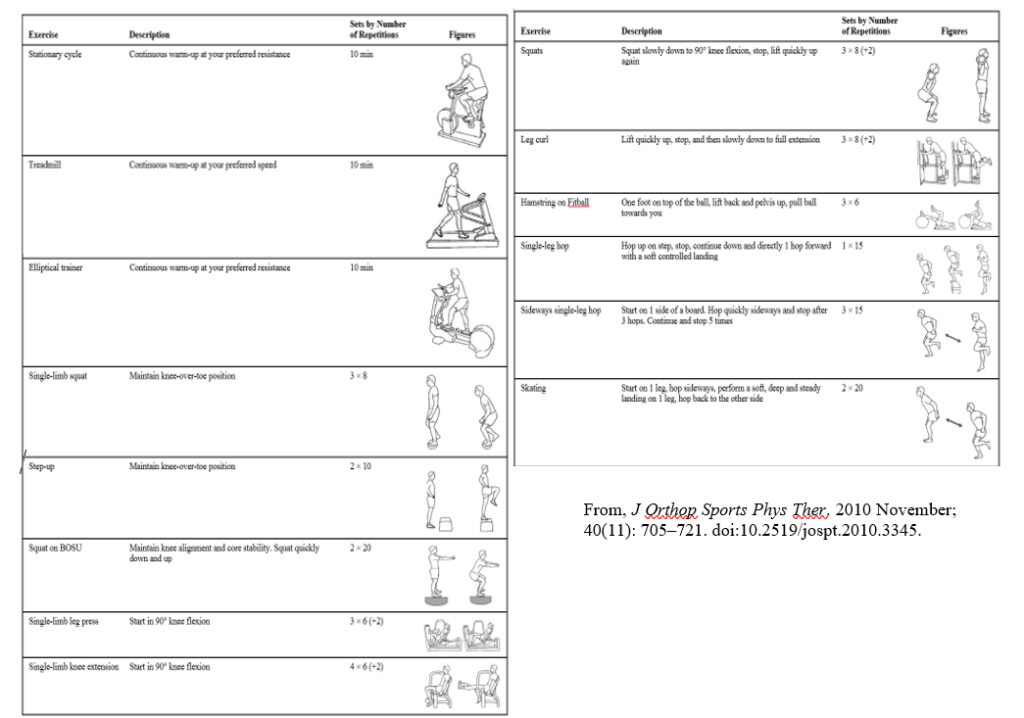
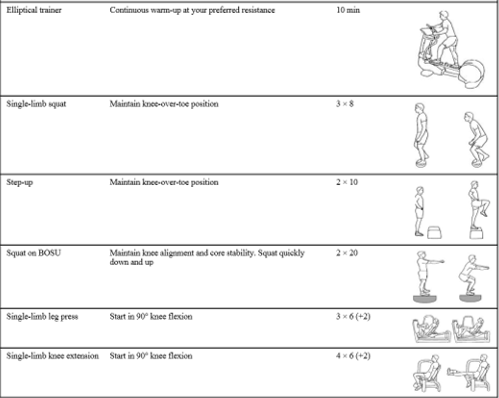
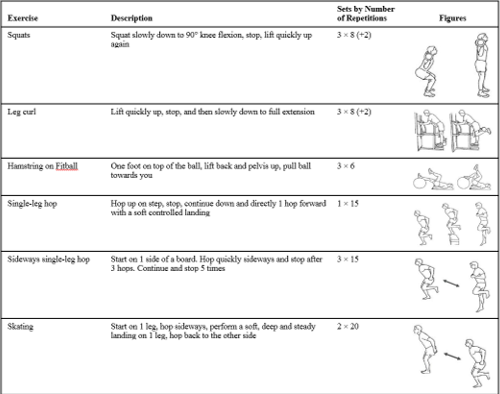
Physical therapists supervised the exercise progression and ensured participants were activating the hip abductors and hip external rotators. Exercises included side-lying hip extension and external rotation, squats with resistance band targeting hip external rotators, hip hikes against the wall, side-stepping with a resistance band to target hip abductors, and then single leg squats with resistance bands targeting hip abductors.
Results
Results show that the treatment group showed significantly improved hip abduction and external rotation strength, and the control group did not. Though the running data did not show any difference in peak hip adduction between groups or between pre- and post-training, single-leg squat data did show significant improvement in peak hip adduction, hip internal rotation, and contralateral (opposite side) pelvic drop.
Discussion and conclusion
The researchers found that their hip abductor/external rotator strength training program was effective at changing hip mechanics during a single-leg squat. However, no changes in running mechanics were noted, which suggests that strengthening the hip muscles alone may not be enough to change movement patterns while running.
Why go to a physical therapist?
A physical therapist (PT) can examine and evaluate an individual’s mechanics while running, squatting, or performing any physical activity. Then the PT can determine what weaknesses and movement patterns may be present. Physical therapists can provide exercises to strengthen and stretch weak and tight muscles, but they can also work on retraining movement patterns that may be associated with injuries. Pure strengthening may not be enough to change the mechanics that may be underlying some injuries in athletes or anyone. For that reason, we may also focus on neuromuscular reeducation to change movement patterns so that we can address the root cause of the problem.
Original article
Willy, R. W., & Davis, I. S. (2011). The Effect of a Hip-Strengthening Program on Mechanics During Running and During a Single-Leg Squat. Journal of Orthopaedic & Sports Physical Therapy,41(9), 625-632. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3470